Optimizing your farm’s irrigation system is crucial for enhancing crop yield, conserving water, and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices. As water resources become increasingly scarce and the demand for food production rises, efficient irrigation management is more important than ever. This article delves into the strategies and technologies that can help farmers optimize their irrigation systems, ensuring that every drop of water is used effectively.
Understanding Your Farm’s Water Needs
Before implementing any changes to your irrigation system, it’s essential to understand the specific water needs of your crops and soil. Different plants have varying water requirements, and factors such as soil type, climate, and growth stage can significantly influence these needs. Conducting a thorough assessment of your farm’s water requirements is the first step towards optimization.
Soil Analysis
Soil type plays a critical role in determining how much water is needed and how often it should be applied. Sandy soils, for example, drain quickly and may require more frequent irrigation, while clay soils retain moisture longer and may need less frequent watering. Conducting a soil analysis can provide valuable insights into the water-holding capacity of your soil, helping you tailor your irrigation schedule accordingly.
Crop Water Requirements
Each crop has its own water needs, which can vary throughout the growing season. Understanding the specific water requirements of your crops at different growth stages is essential for optimizing irrigation. For instance, some crops may require more water during flowering or fruiting stages, while others may need less during early growth. Consulting agricultural extension services or using crop-specific water requirement guides can help you determine the optimal irrigation schedule for your crops.
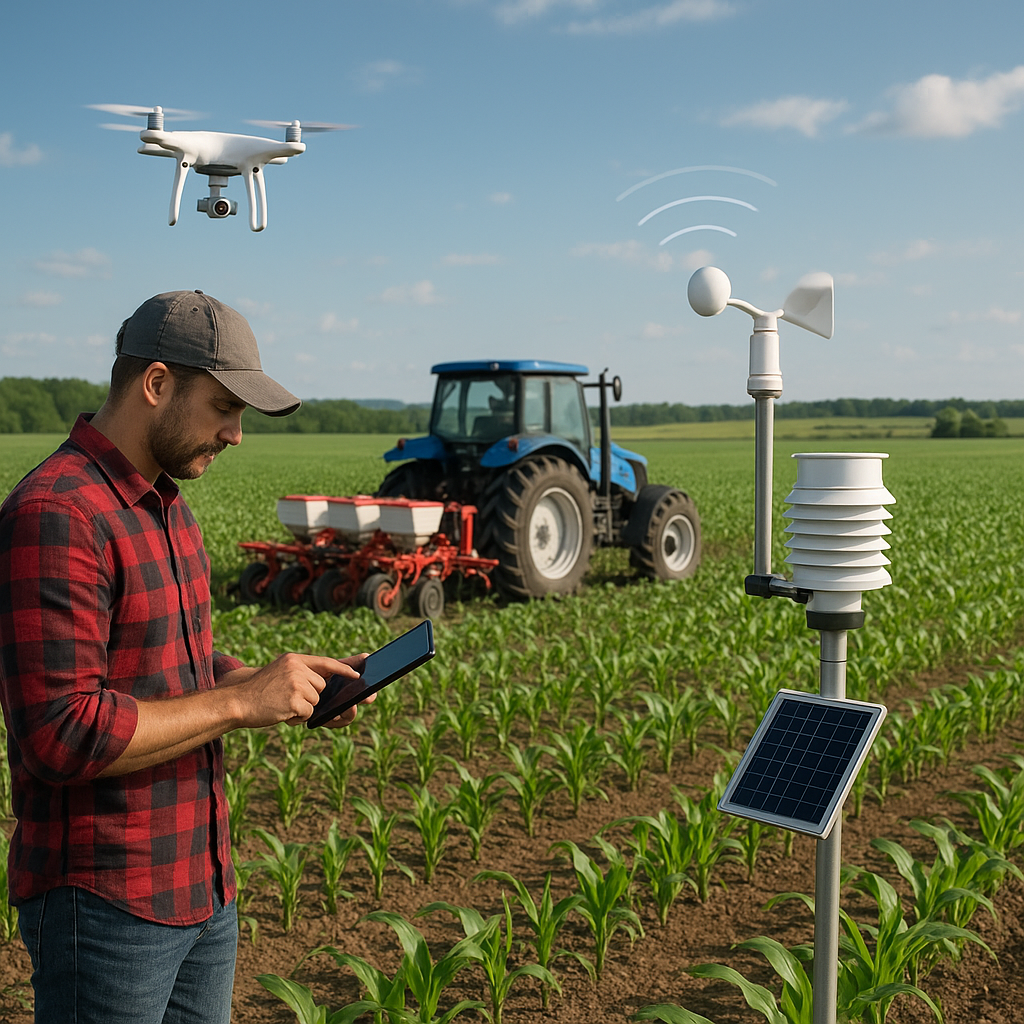
Implementing Advanced Irrigation Technologies
Advancements in irrigation technology have made it possible for farmers to optimize water usage more effectively than ever before. By adopting modern irrigation systems and tools, farmers can ensure precise water application, reduce waste, and improve crop yields.
Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation is one of the most efficient methods of watering crops, as it delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of tubes and emitters. This system minimizes evaporation and runoff, ensuring that water is used efficiently. Drip irrigation is particularly beneficial for row crops, orchards, and vineyards, where precise water application is crucial.
Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers use weather data, soil moisture sensors, and other inputs to adjust watering schedules automatically. These systems can significantly reduce water usage by ensuring that irrigation only occurs when necessary. By integrating smart controllers with your existing irrigation system, you can optimize water application based on real-time conditions, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
Soil Moisture Sensors
Soil moisture sensors provide real-time data on the moisture levels in your soil, allowing you to make informed decisions about when and how much to irrigate. By using these sensors, farmers can avoid overwatering or underwatering, ensuring that crops receive the optimal amount of water. This technology is particularly useful in areas with variable weather conditions, where traditional irrigation schedules may not be effective.
Maximizing Water Efficiency
In addition to implementing advanced technologies, there are several practices that can help maximize water efficiency on your farm. These practices focus on reducing water waste and ensuring that every drop is used effectively.
Mulching
Mulching involves covering the soil surface with organic or inorganic materials, such as straw, wood chips, or plastic. This practice helps retain soil moisture by reducing evaporation, suppressing weeds, and moderating soil temperature. By maintaining consistent soil moisture levels, mulching can reduce the need for frequent irrigation, conserving water and improving crop health.
Rainwater Harvesting
Rainwater harvesting involves collecting and storing rainwater for later use in irrigation. This practice can significantly reduce reliance on groundwater or municipal water sources, especially in regions with seasonal rainfall. By installing rainwater collection systems, such as tanks or ponds, farmers can capture and store rainwater for use during dry periods, ensuring a sustainable water supply for their crops.
Scheduling Irrigation
Properly scheduling irrigation is crucial for optimizing water use. Watering during the early morning or late evening, when temperatures are cooler and evaporation rates are lower, can help conserve water. Additionally, adjusting irrigation schedules based on weather forecasts and soil moisture levels can prevent overwatering and ensure that crops receive the right amount of water at the right time.
Conclusion
Optimizing your farm’s irrigation system is a multifaceted process that involves understanding your farm’s specific water needs, implementing advanced technologies, and adopting water-efficient practices. By taking a comprehensive approach to irrigation management, farmers can enhance crop yields, conserve water, and contribute to sustainable agricultural practices. As water resources become increasingly limited, optimizing irrigation systems will be essential for ensuring the long-term viability of farming operations.